Want to know how trading brokers make money? Learn about their brokerage revenue streams, from commission structures to payment for order flow.
Trading brokers are those intermediaries between market participants and exchanges that allow trading in stocks, ETFs, commodities, mutual funds, foreign exchange, etc. Unlike traditional stockbrokers who focus majorly on equity trading, these brokers provide trading facilities in multiple asset classes.
This blog provides insights into what trading brokers are and how trading brokers make money.
What is a Trading Broker?
Trading brokers have the same function as stock brokers, but the main difference is that a trading broker usually does not charge a trading commission, and they earn their income from different sources. These brokers provide their clients with multiple asset classes like foreign exchange, mutual funds, equity, commodity, etc. Trading brokers nowadays use advanced computers for fast trade execution.
How Trading Brokers Make Money?
Along with the traditional brokerage fees, trading brokers can have multiple brokerage revenue streams that allow them to introduce zero-commission plans and still make money. Let us understand more about these zero-commission broker earnings in detail:
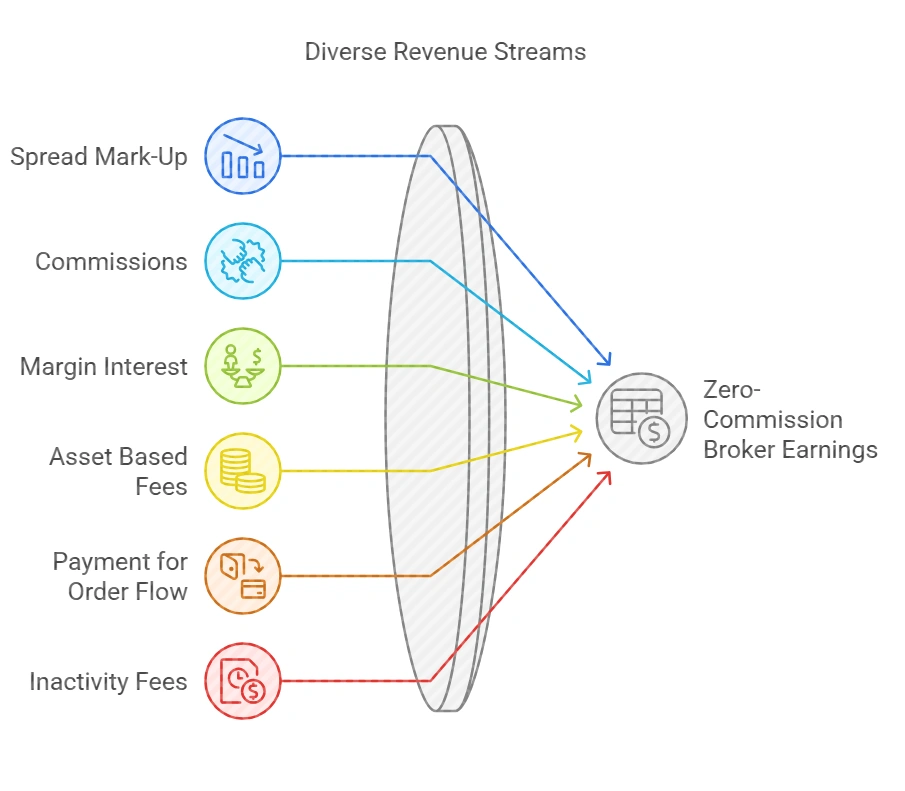
Image showing different sources of income for a trading broker
Spread Mark Up
Bid-Ask Spread means the difference between what price a seller is willing to take for an asset (ask) and what price a buyer is willing to pay (bid). The wider the difference between these, the higher the bid-ask spread. During volatile markets, this spread can widen. Trading brokers try to make this spread wider. For example, the asking price for an asset is ₹100, the bid price is ₹99, and the spread of ₹1 becomes the broker’s profit.
Commission
Commission is a fixed percentage of transaction value or a flat fee per trade. This is an income source for both trading brokers and stock brokers. This is the most common method of how brokers earn money.
Some brokers even provide a monthly fee system where they charge a monthly fee from their clients and allow unlimited trades to be placed.
Full-service brokers charge a much higher commission than online discount brokers for the additional services they provide, such as trading advisory, portfolio management, etc.
Margin Interest
Trading brokers give the facility of margin to their clients. This facility allows traders to borrow money from the broker to take leverage stock positions. The brokers charge interest from their clients based on the money they are lending.
Example: A broker may charge an 8% interest rate on margin loans. If a trader borrows ₹1,00,000, the broker will earn ₹8,000 annually in interest. The interest will be charged for as long as the position stays open.
Asset Based Fees
Basically, brokers with advisory or managed accounts get paid a share of the money they manage. They take a small percentage of your total investment as their fee. This covers things like managing your portfolio and giving you investment tips. These are the management fees similar to those charged by mutual funds and hedge funds.
For instance, if they charge 1% and your portfolio is ₹100,000, they would make ₹1,000 a year. This setup really pushes them to help your investments grow because more money for you means more money for them.
Payment for Order Flow
Payment for order flow explanation is simple, it means some trading brokers are paid by market makers or big market trading firms to channel their client orders to them instead of other market players. This ensures better prices for the market makers.
For example, a market maker who wants to buy certain shares at a certain price can pay the broker to fulfill his orders first as compared to other market participants.
These methods can have legal and ethical implications for the brokers, and this method might be banned in some countries.
Inactivity and Miscellaneous Fees
Traders should be aware of the various fees that brokers may charge, which can include inactivity fees for dormant accounts, currency conversion fees, withdrawal fees, and account maintenance charges. Brokers can earn these fees even if there is no trading activity in a demat account. Even though these fees may appear insignificant, they can add up over time. Consequently, it is crucial for traders to familiarize themselves with the trading broker commission structure before selecting a broker.
How is a trading broker different from a stock broker?
For a better understanding of how trading brokers make money, let us look at the major differences between stockbrokers and trading brokers:
| Criteria | Trading Broker | Stock Broker |
| Meaning | Earn brokerage from sources apart from trading commission | Earn brokerage majorly in the form of commission for executing orders. |
| Brokerage Revenue Streams | Spread mark up, asset based fees, Margin interest, Payment for order flow etc. | Commission as a percentage of transaction value |
| Products Offered | Offers equity, commodity, foreign exchange, currency, etc. | Major focus on Equity |
| Investor Type | Usually attract short term speculators and traders | Usually attracts long term investors. |
| Services | May offer derivative trading, leverage and other facilities | Provides research and personalized financial advice |
Conclusion
The different brokerage revenue streams of trading brokers allow them to introduce zero-commission broking plans. The trading broker commission structures used by these brokers can involve methods like spread markup, payment for order flow, etc. Traders must be aware of zero-commission broker earnings methods before choosing the right broker.