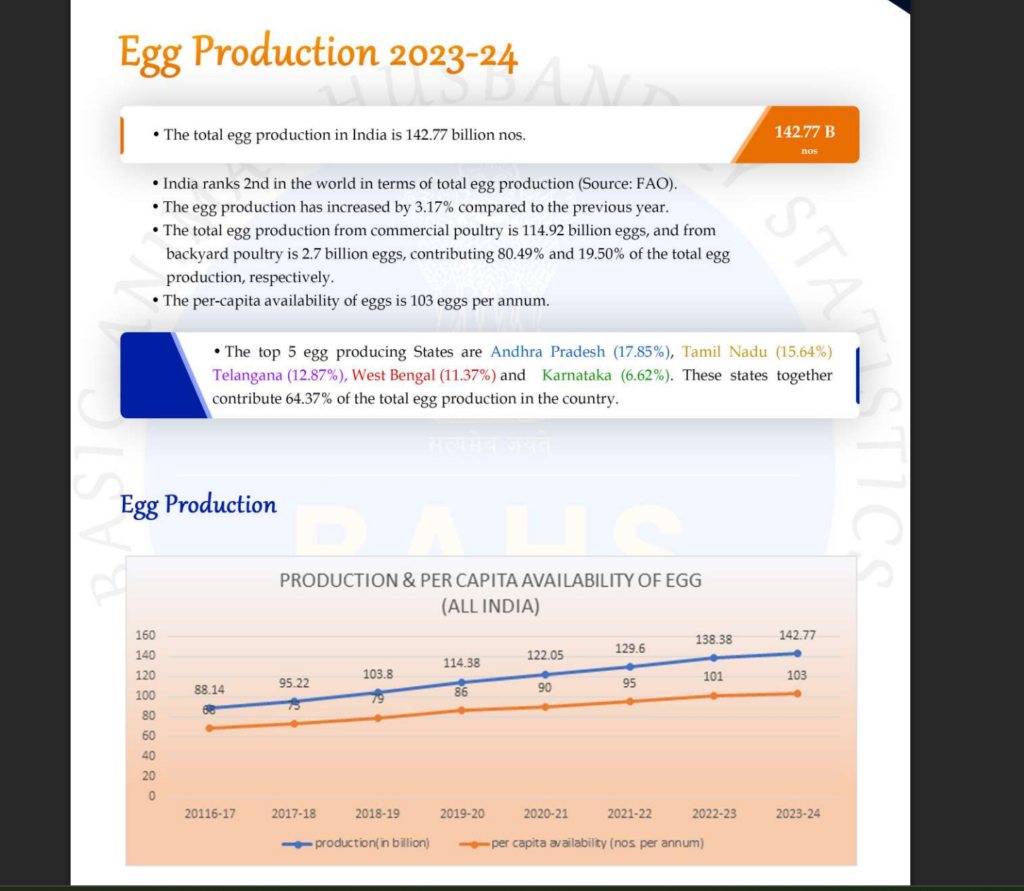
The poultry farming business in India has become a growth sector supported by rising demand for chicken and eggs. The Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying (DAHD) in its recent pronouncement reported the growth of India’s egg production from 78.48 billion in 2014-15 to 142.77 billion in 2023-24, which is approximately equivalent to a CAGR of 6.87% for the period. Poultry farming business in India requires, first of all acquaintance with costs, finance, subsidies, and profits that are realistic.
Understanding the Poultry Farming Sector?
Poultry farming is the practice of raising birds such as chickens (for meat or eggs), ducks, turkeys, etc. In India, the main poultry farming is:
- Broiler farming: the growing of birds intended exclusively for meat production.
- Layer farming: raising hens for egg production.
Initial Investment & Setup Costs
Here’s an estimated cost breakdown for a 1,000-bird poultry unit in India, based on recent project reports:
| Expense | Estimated Cost (₹) |
| Land & Construction | ₹3–5 lakh |
| Equipment (feeders, drinkers, brooders) | ₹50,000–1 lakh |
| Chicks (1,000 @ ~₹40 each) | ~₹40,000 |
| Feed & Medicine (per batch) | ₹1.5–2 lakh |
| Labour & Utilities | ~₹50,000 |
| Miscellaneous & Maintenance | ₹25,000–50,000 |
| Total Estimated Investment | ₹6–9 lakh |
Profit Potential in Poultry Farming
Poultry farming business in India offers strong profit potential due to steady demand for eggs and meat. With proper management, hygiene, and marketing, farmers can earn consistent and scalable income.
- If one model report estimates a net profit of ₹40,000-70,000 from a 6-8 week cycle per broiler batch (1,000 birds), based on the income generated.
- Under favorable conditions, 5-6 batches a year could mean around ₹3-4 lakh net profit per year for a 1,000-bird farm.
- In addition, the more comprehensive datasets from the livestock and poultry sectors suggest strong growth: according to a DAHD press release, the livestock sector (including poultry) recorded a CAGR of ~12.99% from 2014-15 to 2022-23.
Loan Options & Subsidies for Poultry Farming Business in India
Several government schemes and financial institutions in India provide loans and subsidies to support poultry farming setup, infrastructure, and expansion for both small and large-scale farmers.
- NABARD Poultry Scheme
- NABARD provides capital subsidy, for instance, in the amount of 25% of the project cost for the general category, and 33.33% for SC/ST/hilly regions. for the projects carried out in the poultry sector.
- Loans are usually needed to be taken first; the subsidy is at the back.
- PMEGP (Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme)
- This scheme administers a subsidy linked to credit under the MSME sector, which can be utilized for small poultry and agriculture/agribusiness ventures. (Bank and state-specific conditions would be needed to check)
- This scheme administers a subsidy linked to credit under the MSME sector, which can be utilized for small poultry and agriculture/agribusiness ventures. (Bank and state-specific conditions would be needed to check)
- Mudra Loans (Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana)
- For small-cap setups (less than ₹10 Lakhs), the banks may offer a collateral-free loan under the “Mudra” scheme.
- For small-cap setups (less than ₹10 Lakhs), the banks may offer a collateral-free loan under the “Mudra” scheme.
- Commercial Banks / Cooperatives
- Numerous banks provide loans against the agricultural business for poultry. The interest rates are different; the repayment time, loan size depend on the scale.
- Numerous banks provide loans against the agricultural business for poultry. The interest rates are different; the repayment time, loan size depend on the scale.
- Other Government Programmes
- The “National Livestock Mission (NLM)”, “Poultry Venture Capital Fund (PVCF)”, and “Rural Backyard Poultry Development programs” are just some of the schemes that are available, and they provide subsidies or interest subvention. For example, the website of AgriFarming describes in detail the information about the subsidy.
Steps to Start a Poultry Farming Business in India
Initiating a poultry farming venture in India needs planning, breed choice, housing establishment, feeding management, health care, and marketing to be done effectively.
1. Select the kind of poultry (broiler, layer, native/unimproved breed): this is a choice that should take into account the market demand as well as the investment that can be made.
2. Select the right location: Make sure there is enough airflow, good drainage, and a quarantine area (preventing the spread of diseases).
3. Arrange funding: Determine total investment, apply for appropriate loan + subsidy.
4. Secure licenses & permits: Depending on state and scale registration, environmental clearance (if applicable), and food safety license.
5. Buy equipment & chicks: Source from certified hatcheries.
6. Set up feed, healthcare & labour: Careful management of feed that represents 60-70% of expenses in many farms is a must.
7. Selling your produce: Local butcheries, restaurants, supermarkets, or even direct sales are possible channels to connect with.
8. Watching the processes and controlling the risks: Outbreaks of diseases (for instance, avian flu), feed price changes, and market variations could all result in the loss of profits.
Challenges & Risk Factors
Poultry farming is still facing a lot of problems, such as the outbreak of diseases, changes in the price of feed, and market instability that restrict the implementation of biosecurity measures, which eventually lead to reduced production and profit.
- Disease incidence: The population of birds may collapse significantly, especially when the biosecurity measures are not of a high standard.
- Feed cost escalation: Due to the fact that feed accounts for a large portion of the total cost, fluctuations in prices can greatly impact profits.
- Market price fluctuations: A situation when the supply of product exceeds the demand or when the demand for the product drops, will bring about a decrease in the selling price of the product, which could be per bird or per egg.
- Climate & infrastructure: Bad housing, insufficient aeration, and high or low temperatures will have negative impacts on the rate of growth and bird death.
- Capital intensity & repayment risk: When the size is enormous, it becomes almost impossible to avoid taking loans and making payments even if the production is not up to the desired standard.
Conclusion
The Indian poultry farming business is definitely a good option, as it is backed by increasing demand, government support, and easy credit. If an entrepreneur is well-prepared, they can increase the chances of success by doing an accurate investment estimation, selecting the right size of operation, getting the appropriate financing, and handling the daily processes efficiently. Poultry farming can be a real opportunity for rural landowners and agripreneurs, as long as there is a realistic understanding of the profits to be made, the challenges of operating, and the risks involved.
DISCLAIMER: The information given in this blog is for educational purposes only. Any content of this blog is not investment advice.